Difference between revisions of "Pair Trading Models"
(→Model Support) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=== Model Support === | === Model Support === | ||
* in PTL backtester: '''yes''' (max Z-score not supported) | * in PTL backtester: '''yes''' (max Z-score not supported) | ||
| − | * in PTL portfolio backtester: '''yes''' | + | * in PTL portfolio backtester: '''yes''' |
| − | * in PTL Trader: '''yes''' (RSI | + | * in PTL Trader: '''yes''' (RSI supported since v1.2.0) |
=== Model Neutrality === | === Model Neutrality === | ||
Revision as of 22:09, 2 January 2015
Pair Trading Lab offers pair trading algorithms based on various mathematical models. These are models currently supported in PTL:
Contents |
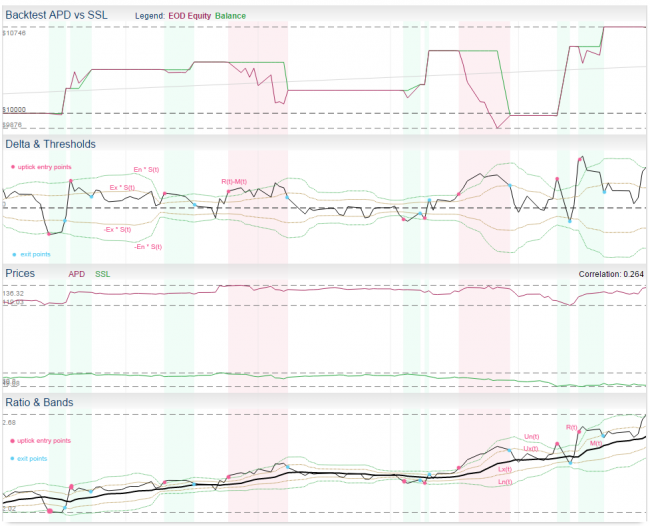
Ratio Model
This is one of the standard pair trading models described in literature. It is based in ratio of instrument prices, moving average and standard deviation. In other words, it is based on Bollinger Bands indicator.
Since Nov 27th 2014, this model also supports additional RSI filter you can use in addition to Bollinger Bands method.
Model Support
- in PTL backtester: yes (max Z-score not supported)
- in PTL portfolio backtester: yes
- in PTL Trader: yes (RSI supported since v1.2.0)
Model Neutrality
We currently support only dollar-neutral version of this model, which means we allocate same amounts of margin to both legs based on current prices at the time of opening the position.
Model Parameters
- entry threshold En for Z-score, typical value range is <1.5, 2.5>, 2.0 is used most often
- exit threshold Ex for Z-score, typical value is <-0.5, 0.5>, 0 is used most often...we allow positive values only for now
- max Z-score Emax (optional, to filter out extremes, typical value is >4 if used)
- moving average period Pm (typical range <10, 100>), default = 15
- moving average type T (algorithm), default = exponential
- standard deviation period Ps (typical range <10, 100>), default = 15
- entry mode (simple, uptick, downtick)
- RSI period and threshold (optional RSI filtering)
Description
- we trade pair of stocks A, B, having price series A(t), B(t)
- we need to calculate ratio time series R(t) = A(t) / B(t)
- let's apply moving average of type T with period Pm on R(t) to get time series M(t)
- let's apply standard deviation with period Ps on R(t) to get time series S(t)
- now we can create Z-score series Z(t) as Z(t) = (R(t) - M(t)) / S(t), this time series can give us z-score to signal trading decision directly
- another common approach (to visualize) is to create bands and put it above the moving average M(t):
- upper entry band Un(t) = M(t) + S(t) * En
- lower entry band Ln(t) = M(t) - S(t) * En
- upper exit band Ux(t) = M(t) + S(t) * Ex
- lower exit band Lx(t) = M(t) - S(t) * Ex
- these bands are actually the same bands as in Bollinger Bands indicator and we can use crossing of R(t) and bands as trade signals
Entering Position
There are certain possible approaches how to interpret model statistics in order to make trading decisions. For entering position, we used to call them entry modes. This is the list of them and description how they work:
- entry mode = simple:
- to open short pair position, it is simple enough if the Z-score Z(t) >= En (equivalent to R(t) >= Un(t))
- to open long pair position, it is simple enough if the Z-score Z(t) <= -En (equivalent to R(t) <= Ln(t))
- entry mode = uptick: same as simple, but in addition, previous Z-score must be below the entry band (so we cross the band from inside to outside):
- to open short pair position, we require Z(t) >= En (equivalent to R(t) >= Un(t)) and Z(t-1) < En (same as R(t-1) < Un(t-1))
- to open long pair position, we require Z(t) <= -En (equivalent to R(t) <= Ln(t)) and Z(t-1) > -En (same as R(t-1) > Ln(t-1))
- entry mode = downtick: we wait for the Z-score crossing back the band from outside to inside:
- to open short pair position, we require Z(t) < En and Z(t-1) >= En and Z(t) > Ex
- when using bands, it is the same as having R(t) < Un(t) and R(t-1) >= Un(t-1) and R(t) > Ux(t)
- to open long pair position, we require Z(t) > -En and Z(t-1) <= -En and Z(t) < -Ex
- when using bands, it is the same as having R(t) > Ln(t) and R(t-1) <= Ln(t-1) and R(t) < Lx(t)
Why do we have the simple entry mode? In normal situations and backtests, it gives same results as the uptick mode. But the difference comes up while trading multiple pairs in portfolio. The simple mode allows you to jump in the position immediately after a new slot is freed, regardless of the previous Z-scores.
Which entry mode is better? Hard to tell, sometimes the uptick, sometimes the downtick. You have to do your homework and decide, which idea suits your trading style better. In general, uptick/simple mode is more aggressive, as it does not wait for first signs of spread mean reversion.
Exiting Position
For exiting position, we always use only these simple rules:
- we exit short position when Z(t) <= Ex (equivalent to R(t) <= Ux(t))
- we exit long position when Z(t) >= -Ex (equivalent to R(t) >= Lx(t))
Moving Average Types
You can choose from these moving average algorithms:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
- Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA)
- Triple Exponential Moving Average (TEMA)
- Triangular Moving Average (TMA)
- Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA)
- MESA Adaptive Moving Average (MAMA)
- Triple Exponential T3 Moving Average
Which one is the best? It depends, you have to test for yourself. They mostly differ in the term of memory and how fast they react to changes. Industry standard and the default is EMA. We suggest to try all of them on some sample pair to see how they work.
RSI Filtering
You can combine the Z-score/Bollinger Band model with RSI indicator applied on the ratio R(t). RSI filter will be automatically enabled if you set RSI threshold to other value than zero. RSI filter is combined with the Z-score rules using AND operator (both entry rule and RSI entry rule must be true to open a position).
You can also change the RSI period if you want (default period = 15).
RSI Threshold is value between 0 and 50. Because RSI indicator value oscillates between 0 and 100 (where 50 = mean), your threshold value is just used to set real thresholds for RSI:
- let's assume RSI Period Pr was entered
- effective RSI value threshold is then 50+Pr (upper) and 50-Pr (lower)
- you can see both thresholds in the example image at the right side
Example:
- RSI Threshold entered is 15
- then, short positions are only opened, if RSI >= 65 (50+15)
- long positions are only opened, if RSI <=35 (50-15)
Useful hint: if you want to control entry rules just by RSI, you can set Entry Mode to simple and Entry Threshold to some low value.
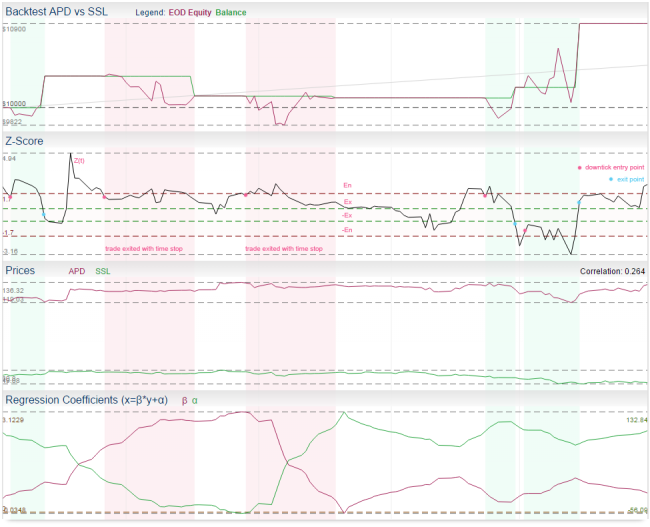
Residual Model
Residual mode is based on linear regression. In literature it has been also referred to as the cointegration approach. Linear regression of both stocks is constructed in order to fit a linear relationship between both instruments and estimate its best parameters using the OLS method (Ordinary Least Squares). Then, standard deviation is applied on the regression residuals to estimate its statistical properties and calculate Z-scores.
This particular implementation is very simple. The regression is constructed using floating window of a fixed period, the same period is used for calculating the standard deviation.
Model Support
- in PTL backtester: yes (max Z-score not supported)
- in PTL portfolio backtester: yes (only simple entry mode supported for now)
- in PTL Trader: yes (only simple entry mode supported for now)
Model Neutrality
We currently support only dollar-neutral version of this model, which means we allocate same amounts of margin to both legs based on current prices at the time of opening the position.
Model Parameters
- entry threshold En for Z-score, typical value range is <1.2, 2.5>, 1.5 is used most often
- exit threshold Ex for Z-score, typical value is <-0.5, 0.5>, 0 is used most often...we allow positive values only for now
- max Z-score Emax (optional, to filter out extremes, typical value is >4 if used)
- linear regression period P (floating window is used), typical range <15, 300>
- entry mode (simple, uptick, downtick)
Description
- we trade pair of stocks A, B, having price series A(t), B(t)
- first we need to construct a linear regression between A(t), B(t) using OLS, where A(t) = β * B(t) + α + R(t)
- because we use floating window of period P (we calculate new regression each day), we actually get new series β(t), α(t), R(t), where β(t), α(t) are series of regression coefficients and R(t) are residuals (prediction errors)
- R(t) = A(t) - (β(t) * B(t) + α(t))
- then we apply standard deviation of period P on residuals R(t) and we put it to S(t)
- now we can create Z-score series Z(t) as Z(t) = R(t) / S(t), this time series can give us z-score to signal trading decision directly
Entering Position
There are certain possible approaches how to interpret model statistics in order to make trading decisions. For entering position, we used to call them entry modes. This is the list of them and description how they work:
- entry mode = simple:
- to open short pair position, it is simple enough if the Z-score Z(t) >= En
- to open long pair position, it is simple enough if the Z-score Z(t) <= -En
- entry mode = uptick: same as simple, but in addition, previous Z-score must be below the entry band (so we cross the band from inside to outside):
- to open short pair position, we require Z(t) >= En and Z(t-1) < En
- to open long pair position, we require Z(t) <= -En and Z(t-1) > -En
- entry mode = downtick: we wait for the Z-score crossing back the band from outside to inside:
- to open short pair position, we require Z(t) < En and Z(t-1) >= En and Z(t) > Ex
- to open long pair position, we require Z(t) > -En and Z(t-1) <= -En and Z(t) < -Ex
Exiting Position
For exiting position, we always use only these simple rules:
- we exit short position when Z(t) <= Ex
- we exit long position when Z(t) >= -Ex
Kalman Model
(under construction)
Model Support
- in PTL backtester: yes (max Z-score not supported)
- in PTL portfolio backtester: not yet
- in PTL Trader: not yet
Model Neutrality
For Kalman Model, we support both dollar neutral (equal dollar amount invested to each leg) and beta neutral regimes.
Model Parameters
- entry threshold En for Z-score, typical value is 1
- exit threshold Ex for Z-score, typical value is 0
- max Z-score Emax (optional, to filter out extremes, typical value is >4 if used)
- Kalman filter transition covariance δ, typical value is 0.0001
- Kalman filter observation covariance Ve, typical value is 0.001
- entry mode (simple, uptick, downtick)
(section under construction)